For years, Amazon.com Inc. (Amazon) has been a force in e-commerce and the overall stock market, selling at more than $2,000 a share. However, many simultaneous events have led to the stock declining since it has failed to meet expectations.
In April 2022, the company’s stock declined 14.0%, its largest one-day drop since July 2006, losing $206.2 billion in market cap, only second to Meta Inc.’s (Meta) decline earlier in the year, as the company missed its earnings per share estimate by 188.99%.
So, what happened?
Investments gone wrong
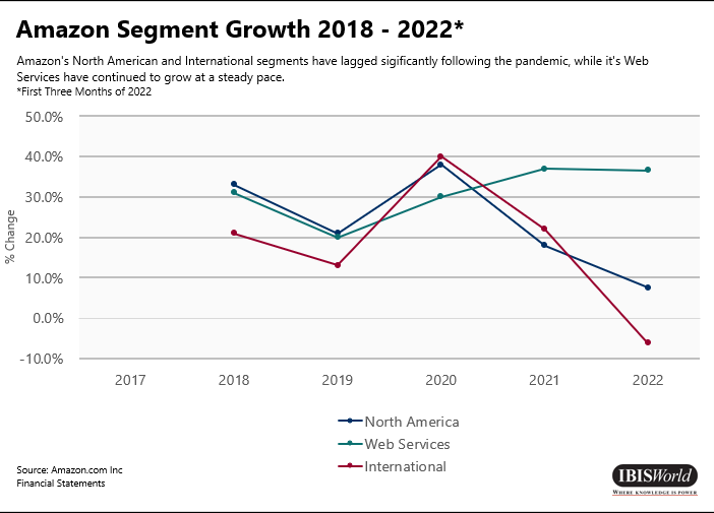
In an attempt to go green, Amazon invested a 17.7% stake in Rivian Automotive Inc. (Rivian), an electric vehicle manufacturer and technology company. In its 2022 Q1 report, Rivian shares declined more than 50.0%, causing Amazon to take a $7.6 billion loss.
Rivian has failed to live up to its own expectations since it is estimated to produce 25,000 electric vehicles in 2022, half the amount it forecast during its 2020 IPO roadshow.
While Rivian offers consumers an alternative option for electric vehicles, supply chain issues stemming from the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic have significantly hindered its production.
Conversely, the company was recently approved to build a second assembly plant in Georgia to increase production output, providing a glimmer of hope for investors.
However, the battery and semiconductor shortages still place a grey cloud over the company’s short-term future.
Consumer trends reverse
During the coronavirus pandemic, Amazon’s revenue skyrocketed as demand for e-commerce platforms grew amid health and safety regulations.
While many e-commerce sites specialize in certain products, Amazon offers a multitude of items including food, entertainment, household items and more.
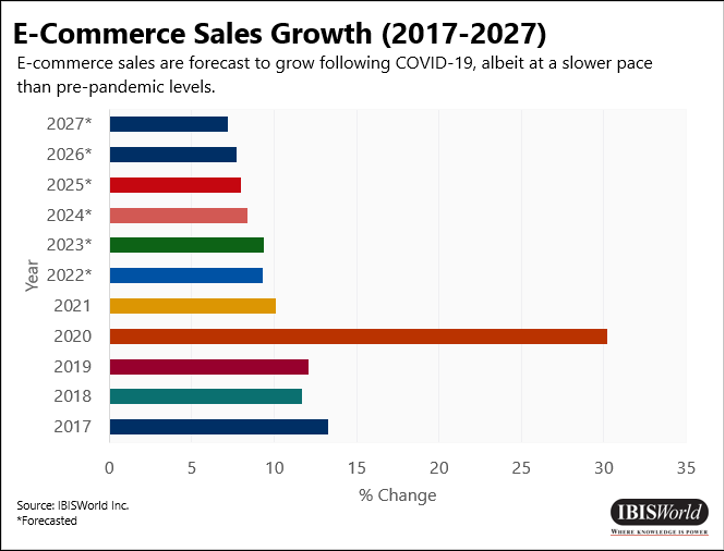
This wide selection, coupled with its premium membership, Amazon Prime, which offered 2-day shipping at $14.99 per month, made Amazon the go-to retailer for most consumers. As a result of the pandemic, e-commerce sales increased 30.2% in 2020 alone.
While e-commerce sales boomed, they deaccelerated in 2021 and are forecast to continue growing at a slower rate in 2022. This is primarily due to the relaxation of health and safety regulations, which has resulted in more consumers shopping at traditional brick-and mortar-establishments.
Furthermore, rising inflation has caused consumers to pull back on discretionary spending altogether as goods have become increasingly more expensive.
According to Mastercard SpendingPulse, e-commerce transactions have declined 1.8% on a year-to-year basis, while in-store sales increased 10.0% during the same period. The slowdown in the e-commerce market affected not only Amazon, but also other companies such as Etsy Inc., Shopify Inc. and Wayfair Inc.
What does the future hold?
While Amazon’s stock is still above prepandemic levels, it has fallen off drastically from its 52-week high of $3,773.08.
Thought it will take a while for Amazon to reach those heights again, the company is slowly adapting to consumer trends. For example, the company announced the opening of its first physical clothing store in May 2022, where customers can try on selected clothes purchased through the company’s app.
While inflationary pressures will continue to impede Amazon's e-commerce operations, the company's continued improvement in its cloud business is expected to partially offset this and help it in the foreseeable future.