IBISWorld Platform
Answer any industry question in minutes with our entire database at your fingertips.

Revenue for the Gas Station industry in China is expected to total $243.3 billion in 2024, up 3.5% from 2023, with annualized growth of 1.7% over the past five years. There are about 115,228 gas stations in China, employing 212,144 people with an estimated payroll of $4.6 billion.Firms in this industry are unable to pass on higher costs to consumers due to government price controls on fuel. Petroleum product prices are controlled by the Chinese Government, specifically by the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Thus, the industry is not highly profitable, particularly in years when international oil and petroleum prices increase and domestic prices are kept at a lower level.The industry is also heavily influenced by the vertical integration of the oil duopoly of China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec) and PetroChina Company Limited (PetroChina). They control crude oil mining and the importation of petroleum products, and they own most of the large refineries in China. These two firms also jointly own almost half the gas stations in China. Sinopec and PetroChina gas stations have incomparable competitive advantages in fuel supply, funding and technologies. The domestic oil giants have been reducing their oil wholesale in recent years and expanding their retail networks, which has put pressure on small and private filling stations.Over the next five years, the industry is forecast to grow at an annualized rate of 3.4% to $288.2 billion in 2029. Sinopec and PetroChina are expected to maintain their dominant position in the near future, despite growing competition from foreign investment and new domestic companies. Growth will be driven by the rising number of automobiles, the reform on the current pricing mechanism for automotive fuels, intensified competition, lower global crude oil prices, and the development of non-fuel businesses.
Answer any industry question in minutes with our entire database at your fingertips.
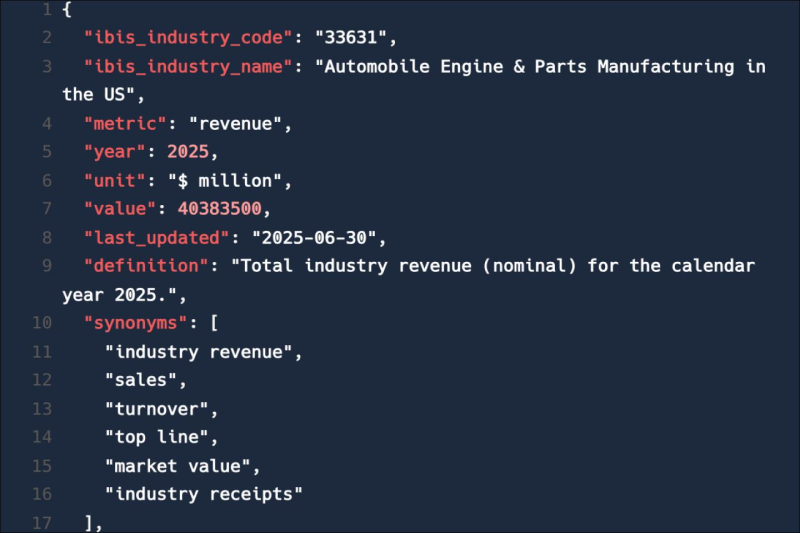
Feed trusted, human-driven industry intelligence straight into your platform.
Streamline your workflow with IBISWorld’s intelligence built into your toolkit.
IBISWorld's research coverage on the Gas Stations industry in China includes market sizing, forecasting, data and analysis from 2014-2029. The most recent publication was released November 2024.
The Gas Stations industry in China operates under the industry code 6564. Establishments in the Gas Stations industry in China retail automotive fuels, like gasoline and diesel oil, and related automotive products, like lubricating oil. Related terms covered in the Gas Stations industry in China include refined oil, kerosene and lubricating oil .
Products and services covered in Gas Stations industry in China include Gasoline, Diesel oil and Lubricating oil.
Companies covered in the Gas Stations industry in China include China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation, PetroChina Company Limited and Shell (China) Limited.
The Performance chapter covers detailed analysis, datasets, detailed current performance, sources of volatility and an outlook with forecasts for the Gas Stations industry in China.
Questions answered in this chapter include what's driving current industry performance, what influences industry volatility, how do successful businesses overcome volatility, what's driving the industry outlook. This analysis is supported with data and statistics on industry revenues, costs, profits, businesses and employees.
The Products and Markets chapter covers detailed products and service segmentation and analysis of major markets for the for the Gas Stations industry in China.
Questions answered in this chapter include how are the industry's products and services performing, what are innovations in industry products and services, what products or services do successful businesses offer and what's influencing demand from the industry's markets. This includes data and statistics on industry revenues by product and service segmentation and major markets.
The Geographic Breakdown chapter covers detailed analysis and datasets on regional performance of the Gas Stations industry in China.
Questions answered in this chapter include where are industry businesses located and how do businesses use location to their advantage. This includes data and statistics on industry revenues by location.
The Competitive Forces chapter covers the concentration, barriers to entry and supplier and buyer profiles in the Gas Stations industry in China. This includes data and statistics on industry market share concentration, barriers to entry, substitute products and buyer & supplier power.
Questions answered in this chapter include what impacts the industry's market share concentration, how do successful businesses handle concentration, what challenges do potential industry entrants face, how can potential entrants overcome barriers to entry, what are substitutes for industry services, how do successful businesses compete with substitutes and what power do buyers and suppliers have over the industry and how do successful businesses manage buyer & supplier power.
The Companies chapter covers Key Takeaways, Market Share and Companies in the Gas Stations industry in China. This includes data and analysis on companies operating in the industry that hold a market share greater than 5%.
Questions answered in this chapter include what companies have a meaningful market share and how each company is performing.
The External Environment chapter covers Key Takeaways, External Drivers, Regulation & Policy and Assistance in the Gas Stations industry in China. This includes data and statistics on factors impacting industry revenue such as economic indicators, regulation, policy and assistance programs.
Questions answered in this chapter include what demographic and macroeconomic factors impact the industry, what regulations impact the industry, what assistance is available to this industry.
The Financial Benchmarks chapter covers Key Takeaways, Cost Structure, Financial Ratios, Valuation Multiples and Key Ratios in the Gas Stations industry in China. This includes financial data and statistics on industry performance including key cost inputs, profitability, key financial ratios and enterprise value multiples.
Questions answered in this chapter include what trends impact industry costs and how financial ratios have changed overtime.
The Industry Data chapter includes 10 years of historical data with 5 years of forecast data covering statistics like revenue, industry value add, establishments, enterprises, employment and wages in the Gas Stations industry in China.
More than 6,000 businesses use IBISWorld to shape local and global economies
We were able to supplement our reports with IBISWorld’s information from both a qualitative and quantitative standpoint. All of our reporting now features some level of IBISWorld integration.

IBISWorld delivers the crisp business knowledge we need to drive our business. Whether it be serving up our major clients, winning new business or educating on industry issues, IBISWorld brings real value.

IBISWorld has revolutionised business information — which has proved commercially invaluable to exporters, investors and public policy professionals in Australia and overseas.

When you’re able to speak to clients and be knowledgeable about what they do and the state that they operate in, they’re going to trust you a lot more.

The market size of the Gas Stations industry in China is $243.3bn in 2026.
There are 34,034 businesses in the Gas Stations industry in China, which has declined at a CAGR of 1.2 % between 2019 and 2024.
The Gas Stations industry in China is unlikely to be materially impacted by import tariffs with imports accounting for a low share of industry revenue.
The Gas Stations industry in China is unlikely to be materially impacted by export tariffs with exports accounting for a low share of industry revenue.
The market size of the Gas Stations industry in China has been growing at a CAGR of 1.7 % between 2019 and 2024.
Over the next five years, the Gas Stations industry in China is expected to grow.
The biggest companies operating in the Gas Stations industry in China are China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation, PetroChina Company Limited and Shell (China) Limited
Gasoline and Diesel oil are part of the Gas Stations industry in China.
The company holding the most market share in the Gas Stations industry in China is China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation.
The level of competition is moderate and decreasing in the Gas Stations industry in China.




